

Under GAAP standards, companies are required to disclose material information that enables their viewers – in particular, its shareholders, lenders, etc. there are potential catalysts that could raise significant concerns – the company’s financials should still be prepared on a going concern basis. Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Prentice-Hall.FASB Going Concern Disclosure Requirements (Source: FASB 205)Įven if the company’s future is questionable and status as a going concern appears to be in question – e.g. Inside Arthur Andersen: Shifting Values, Unexpected Consequences.
#Principal definition in accounting how to
Financial Shenanigans: How to Detect Accounting Gimmicks and Fraud on Financial Reports. Available online at (accessed August 11, 2003). Further readingsįinancial Accounting Standards Board Website. Sarbanes-Oxley also requires chief executive officers and chief financial officers of publicly held companies to provide a statement attesting to the veracity of their financial statements. Accounting firms that audit publicly held companies are required to register with the board, which has the authority to inspect audits. Among the provisions of Sarbanes-Oxley was the creation of the five-member Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, overseen by the SEC. bush signed the sarbanes-oxley Act, which established new regulations for accounting reform and investor protection. Andersen was found guilty of Obstruction of Justice by a jury in Houston, Texas, in June 2002. After the company declared Bankruptcy in 2001, Arthur Andersen came under attack because its auditors had signed off on Enron's financials despite numerous misgivings. In the case of Enron, for example, the company manipulated its financial information to give the appearance that revenues were much higher than they actually were. In the 2000s, companies faced increased scrutiny in light of the widely publicized cases involving such major corporations as Enron and World-Com, along with the firm of Arthur Andersen, one of the world's largest accountancy firms. Specifically, the Securities Act and the Securities Exchange Act established a requirement that publicly held companies must undergo an external audit by an independent accountant once a year. Publicly held companies are required to conform to GAAP standards. For example, the Canadian Institute of Chartered Accountants (CICA) sets GAAP standards in Canada. Other countries have their own GAAP rules, which are set by their versions of the FASB.

Among the organizations that influence GAAP rules are the AICPA and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). The FASB is also monitored by the Corporation Finance division of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). FASAC is overseen by the Financial Accounting Foundation, an independent organization whose 16-member board of trustees chooses FASAC's 33 members. Essentially, FASAC serves as FASB's sounding board. These 33 individuals meet quarterly to discuss accounting issues and gather information, which they then present to FASB. The Financial Accounting Standards Advisory Council (FASAC), which is composed of 33 members from both the public and private sectors, advises the FASB on matters that may affect or influence GAAP rules. In 1973, the responsibility was taken over by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), which was established the same year. The task of creating and maintaining accounting standards was handled by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) from 1936 until 1973. Among other things, these acts established a methodology for standardizing accounting practices among publicly held companies. In response to the Stock Market crash of 1929 and the ensuing Great Depression, Congress passed the Securities Act in 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act in 1934.
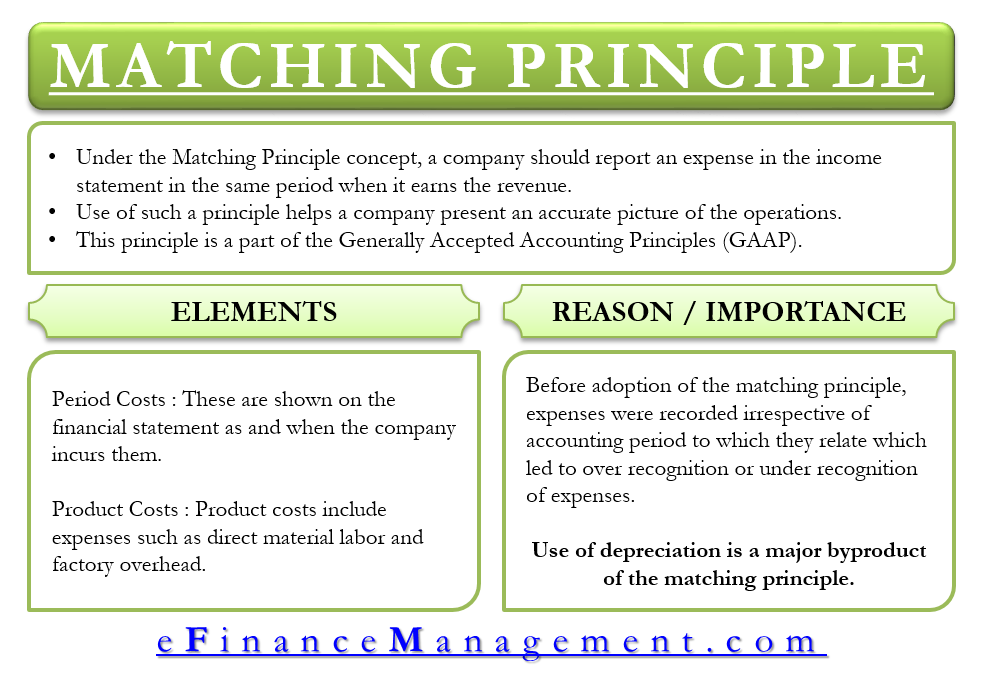
For example, accountants use GAAP standards to prepare financial statements. Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) provide companies and accountants with a consistent set of guidelines that cover both broad accounting principles and specific practices. The standard accounting rules, regulations, and procedures used by companies in maintaining their financial records.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
